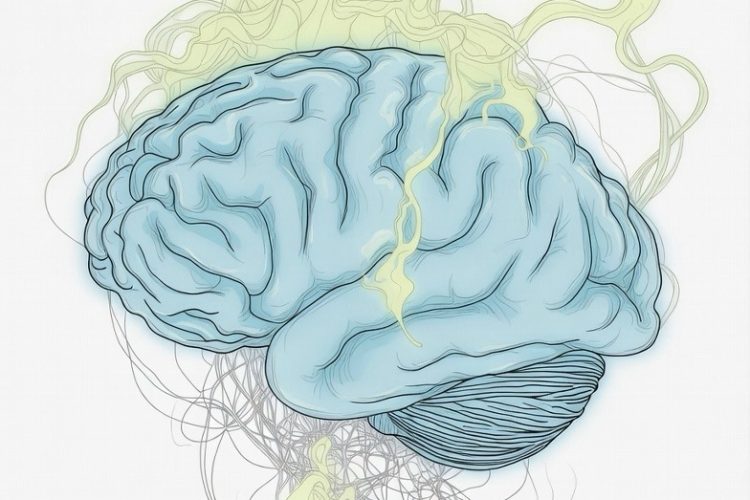
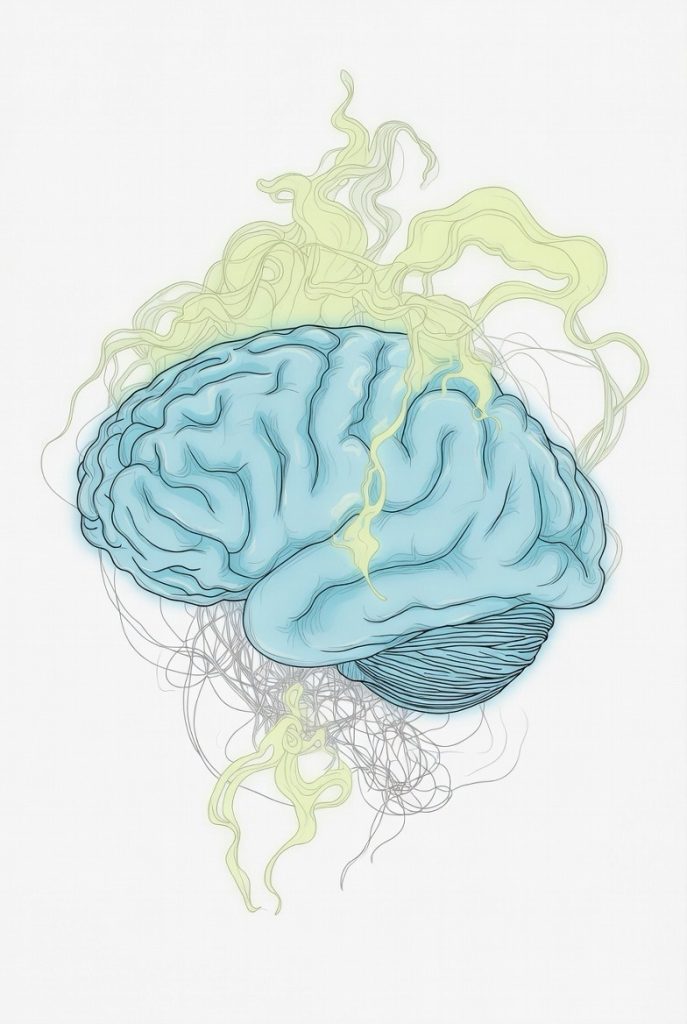
Alzheimer’s disease causes progressive dementia, cognitive decline, memory loss, and motor issues in millions. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), the “rotten egg” gas linked to flatulence, serves as a natural signaling molecule that supports brain health. A 2021 Johns Hopkins study in Alzheimer’s-like mice showed that a slow-release H2S donor (like NaGYY) reduced tau tangles by sulfhydrating the enzyme GSK3β, cutting β-amyloid plaques, easing brain inflammation, and boosting mitochondrial function. Treated mice saw memory and motor skills improve by about 50%. H2S also fights oxidative stress via Nrf2 activation. Importantly, benefits come from controlled medical compounds—not smelling farts, as uncontrolled exposure can be harmful. As of December 2025, this remains promising preclinical research with no proven human treatments yet, though studies continue exploring H2S donors for neurodegeneration and healthy aging.
Long Version
Exploring Hydrogen Sulfide’s Potential in Combating Alzheimer’s Disease: Insights from Groundbreaking Research
Alzheimer’s disease stands as one of the most prevalent forms of neurodegeneration, affecting millions worldwide and leading to progressive dementia. This condition, characterized by cognitive decline and an aging brain that struggles with memory improvement and motor function, poses significant challenges to brain health. As researchers delve deeper into neuroprotective strategies, an unexpected gasotransmitter—hydrogen sulfide, often dubbed the “rotten egg gas”—has emerged as a focal point in scientific discovery. While popularly associated with flatulence and farts, hydrogen sulfide’s role in health extends far beyond such notions, serving as a vital gas signaling molecule in cellular processes.
The Landmark 2021 Study
The intrigue surrounding hydrogen sulfide intensified with a pivotal 2021 research study from Johns Hopkins University, which highlighted its potential benefits in Alzheimer’s-like conditions. In this mice study, scientists utilized an animal model to explore how a slow-release hydrogen sulfide compound could influence key pathological features of the disease. Specifically, the study employed H2S donors, such as NaGYY (a derivative of sodium GYY4137), to administer controlled doses of this compound to transgenic mice engineered to mimic Alzheimer’s pathology. These models included APP/PS1 transgenic mice and 3xTg-AD mice, which exhibit hallmarks like tau tangles and β-amyloid plaques, contributing to spatial memory impairment and hippocampal neuroinflammation.
At the core of the findings was hydrogen sulfide’s ability to reduce tau hyperphosphorylation, a process where excessive phosphorylation leads to the formation of tau tangles that disrupt neuronal function. The mechanism involves sulfhydration, a form of chemical sulfhydration where hydrogen sulfide modifies proteins through protein sulfhydration. In particular, it targets GSK3β, an enzyme that, when overactive, promotes tau hyperphosphorylation. By sulfhydrating GSK3β, hydrogen sulfide inhibits its activity, thereby preventing the buildup of these damaging tangles. This intervention resulted in remarkable improvements: memory and motor function enhanced by approximately 50% in the treated mice, offering a glimpse into potential avenues for addressing cognitive decline.
Mechanisms of Action
Hydrogen sulfide operates through intricate biochemical pathways to exert its neuroprotective effects. As a gas signaling molecule, it facilitates sulfhydration of key proteins, modulating their function to counteract neurodegenerative processes. Beyond inhibiting GSK3β, it influences Aβ production by reducing the accumulation of β-amyloid plaques, which are central to Alzheimer’s pathology. This reduction helps alleviate hippocampal neuroinflammation, a contributor to neuronal damage and cognitive deficits.
Additionally, hydrogen sulfide supports mitochondrial function and cellular bioenergetics, essential for energy production in brain cells. It activates Nrf2, a transcription factor that enhances the brain’s defense against oxidative stress, a common factor in neurodegeneration. These actions collectively improve spatial memory impairment and overall brain resilience, particularly in an aging brain susceptible to dementia.
Broader Neuroprotective Effects
Recent investigations have expanded on these initial findings, revealing hydrogen sulfide’s role in broader aspects of brain health. For instance, it has shown promise in reducing oxidative stress and Aβ deposits, further solidifying its status as a silent neuroprotector. Studies in various animal models, including those induced with streptozotocin to simulate cognitive impairment, demonstrate that systemic administration of hydrogen sulfide donors like NaHS can improve performance in tasks assessing passive avoidance and memory retention.
Hydrogen sulfide’s benefits extend to related conditions, such as traumatic brain injury and other forms of cognitive impairment, where its downregulation is often observed. By restoring H2S levels, researchers have noted enhancements in learning and memory regulation, highlighting its therapeutic importance in neurodegenerative disorders beyond Alzheimer’s.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
It’s important to clarify misconceptions that have arisen from popularized interpretations of this research. While hydrogen sulfide is indeed a component of flatulence—hence the “rotten egg” smell—the study’s benefits stem from precise hydrogen sulfide delivery molecules, not from smelling farts or casual exposure. Sensational claims linking farts to Alzheimer’s prevention overlook the controlled, therapeutic context of H2S donors. In fact, unregulated exposure to hydrogen sulfide can be harmful, emphasizing the need for scientific rigor over anecdotal claims.
Recent Developments and Healthy Aging Implications
Building on the 2021 findings, subsequent research through 2025 has continued to explore hydrogen sulfide’s signaling in neurodegenerative diseases. Reviews and studies have illuminated its nuanced interactions in cerebrovascular and cardiovascular pathologies associated with Alzheimer’s, as well as its potential in healthy aging. Drugs that release tiny amounts of hydrogen sulfide are being investigated for their ability to promote longer, healthier lives by supporting mitochondrial function and reducing neuroinflammation.
Plant-derived hydrogen sulfide delivery compounds are also under scrutiny for preventing β-amyloid aggregation early in disease progression. These advancements underscore hydrogen sulfide’s multifaceted role as a gasotransmitter that could modulate neuroinflammation and enhance cellular bioenergetics, offering new strategies for preserving brain health in an aging population.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite these encouraging results from mice studies, it’s crucial to note that this remains primarily animal model research with no definitive human proof as of late 2025. Human trials are needed to validate whether H2S donors can safely translate to improvements in memory, motor function, and overall cognitive decline in people with dementia. Ongoing investigations into hydrogen sulfide donors continue to refine delivery methods, aiming to harness its neuroprotective properties without the risks associated with the gas’s natural forms.
Future research may focus on developing targeted therapies that restore H2S signaling in preclinical models of Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and other conditions, potentially broadening its applications.
Conclusion
In summary, the 2021 Johns Hopkins scientific discovery has positioned hydrogen sulfide as a promising agent against Alzheimer’s disease, acting through mechanisms like sulfhydration of GSK3β, reduction of tau tangles, and enhancement of Nrf2 activation. While myths about smelling farts persist, the focus remains on sophisticated H2S donors that could revolutionize treatment for neurodegeneration. As research progresses, this gas signaling molecule may offer new hope for preserving brain health in an increasingly aging population, provided future studies bridge the gap from mice to humans.
Hashtags For Social Media
Alzheimers #AlzheimersAwareness #Dementia #BrainHealth #Neuroscience #MentalHealth #Health #Wellness #EndAlz #AlzheimersResearch #DementiaAwareness #Neuroprotection #Science #MedicalResearch #BrainPower #HealthyAging #Memory #Neuroplasticity #HealthScience #MentalHealthAwareness #Biohacking #Neurology #Healthylifestyle #BrainTraining #OxidativeStress #AlzheimersDisease #HealthyBrain #Mindfulness #HealthTips #ScientificDiscovery
Related Questions, Words, Phrases
does smelling farts prevent alzheimer’s | can hydrogen sulfide help with alzheimer’s disease | rotten egg gas and brain health benefits | h2s donors in alzheimer’s mice study | johns hopkins hydrogen sulfide alzheimer’s research | does fart gas protect against dementia | hydrogen sulfide reduces tau tangles | smelling your own farts alzheimer’s study | h2s boosts memory in alzheimer’s mice | rotten egg gas guards against alzheimer’s | hydrogen sulfide neuroprotective alzheimer’s | can smelling farts boost brain power | h2s sulfhydration gsk3β alzheimer’s | latest hydrogen sulfide dementia research 2025 | is the fart alzheimer’s myth true