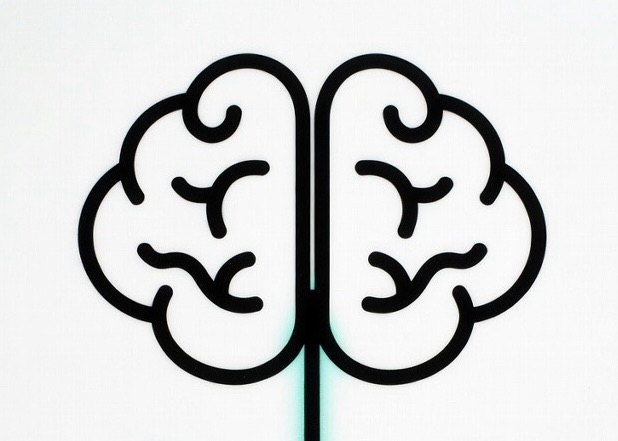
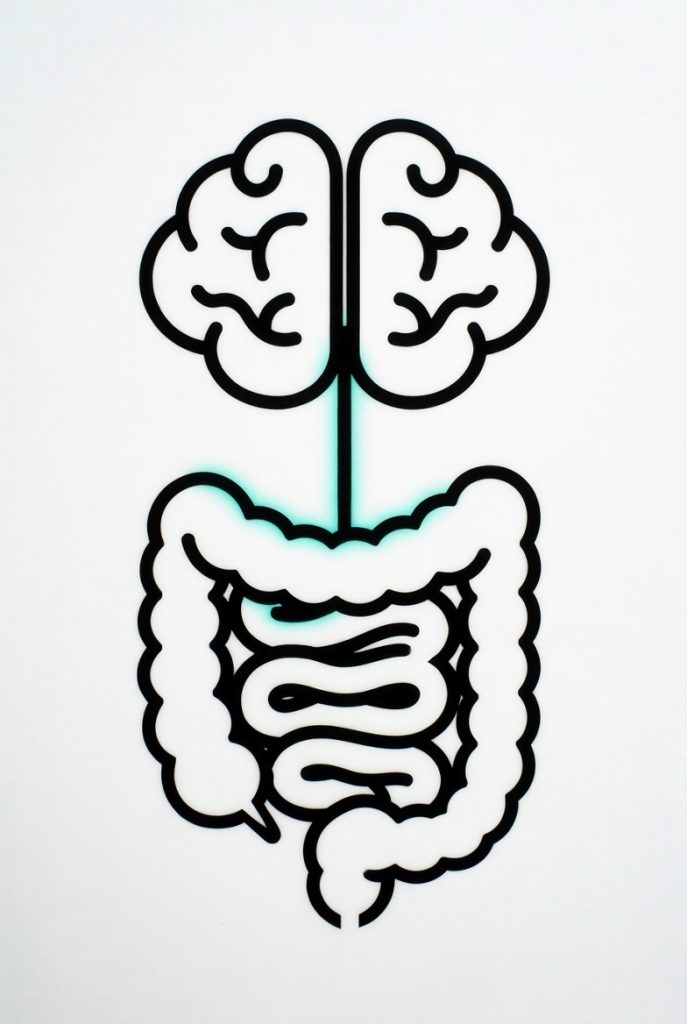
The gut-brain axis shows that gut bacteria produce most of the body’s serotonin and other neurotransmitters that shape mood, emotions, and even our sense of self and comfort. This means digestion and the gut microbiome play a major role in mental health—poor gut health is linked to higher rates of depression, anxiety, and other disorders. Improving diet, adding probiotics, reducing inflammation, and supporting microbial diversity can directly ease mental health symptoms for many people. However, mental health is not purely biological or just a matter of “managing the internal ecosystem.” Psychological factors like thought patterns, trauma, and learned behaviors still matter, and therapies like CBT work even without changing the gut. Social support, stress, and lifestyle also contribute. The most accurate view is integrated: gut health is a powerful, often underused lever that can make psychological efforts and willpower far more effective, but it does not replace them entirely.
Related Questions, Words, Phrases
how does gut health affect mental health | what is the gut-brain axis | why does my gut influence my mood | is mental health linked to digestion | best probiotics for anxiety and depression | how to improve mental health through gut health | guide to gut microbiome and mental wellness | does gut bacteria cause depression | what foods boost serotonin via gut | top ways to heal gut for better mood | why is mental health not just willpower | can fixing gut health cure anxiety | best diet for gut-brain connection | how to balance gut microbiome for mental clarity | connection between gut health and willpower in mental health