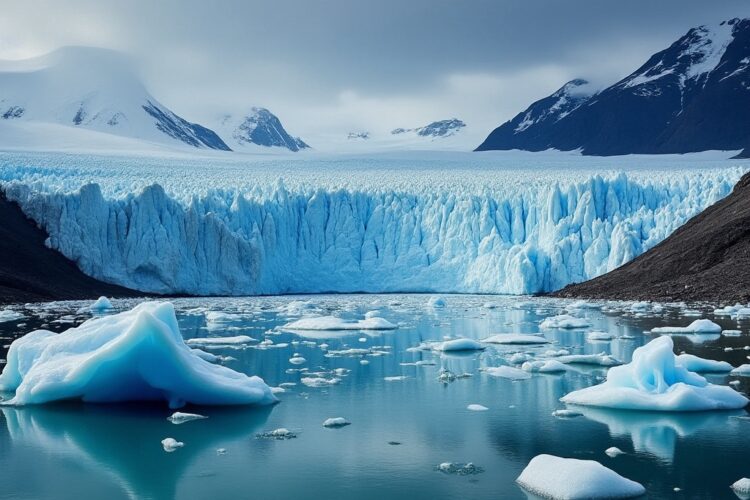
Glaciers around the world are melting at an accelerating rate due to the warming of the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans. The exact speed of melting varies by location and time of year, but in general, the rate of melting has increased significantly over the past few decades. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), glaciers have lost a total of 4,900 billion tonnes of ice since 1992, resulting in an average sea level rise of around 14 millimeters. The rate of melting is expected to continue to increase, leading to significant impacts on sea level rise, water availability, and natural ecosystems.
Long Answer
Glaciers are melting at an alarming rate due to global warming caused by human activities. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has warned that if global warming continues at the current rate, glaciers could shrink by 80% by the end of the century. This article will delve into the current state of glacier melting and its potential consequences.
Glacier melting is a complex process affected by many factors, including temperature, precipitation, and humidity. However, the primary driver of glacier melting is rising temperatures. According to NASA, the average global temperature has increased by 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degree Celsius) since the late 1800s, with the majority of the warming occurring in the last few decades. This rise in temperature has caused glaciers to lose mass, which has implications for sea level rise and freshwater resources.
Glacier melting is occurring worldwide, but some regions are more affected than others. For example, in the Himalayas, home to some of the largest glaciers outside of the polar regions, glaciers are losing an average of 8 billion tons of ice each year. In Alaska, glaciers are losing about 75 billion tons of ice annually. In South America, the Andean glaciers are losing an average of 50% of their mass in the last 50 years.
In Antarctica, the melting rate of glaciers has tripled in the last decade, causing global sea levels to rise by an average of 0.4 inches (1 centimeter) per decade. However, the biggest concern in Antarctica is the potential melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which could raise sea levels by up to 10 feet (3 meters) if it were to melt entirely.
One of the most immediate consequences of glacier melting is sea level rise. As glaciers melt, water is added to the oceans, causing sea levels to rise. The IPCC estimates that sea levels could rise by up to 3 feet (1 meter) by the end of the century, putting coastal cities and low-lying islands at risk of flooding.
Another consequence of glacier melting is the impact on freshwater resources. Glaciers act as natural reservoirs, storing water in the winter and releasing it in the summer when it is needed for agriculture, hydroelectric power, and drinking water. As glaciers shrink, the availability of freshwater resources in some regions could be reduced, affecting millions of people.
In addition to the impact on sea levels and freshwater resources, glacier melting also has consequences for ecosystems. For example, many species rely on glacier-fed streams and rivers for their survival, including salmon in Alaska and Andean bears in South America. As glaciers shrink, these ecosystems could be disrupted, leading to the extinction of some species.
In conclusion, glacier melting is occurring at an alarming rate due to rising temperatures caused by human activities. This melting has consequences for sea level rise, freshwater resources, and ecosystems. It is important that we take immediate action to reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and slow down global warming to mitigate the impacts of glacier melting.
Words Worth Noting
Glacier melting, Global warming, Climate change, Sea level rise, Freshwater resources, Ecosystems, Biodiversity, Greenhouse gas emissions, Renewable energy, Carbon footprint, Sustainability, Environment, Nature, Melting ice, Climate action, Climate justice, Climate crisis, Climate emergency, Activism, Ocean acidification, Polar ice caps, Wildlife conservation, Clean energy, Environmental impact, Carbon dioxide, Methane, Temperature rise, Coastal cities, Low-lying islands, Human impact.
Hashtags For Social Media
#climatechange #globalwarming #glaciermelting #environment #sustainability #savetheplanet #climateaction #earth #nature #meltingice #sealevelrise #freshwaterresources #ecosystems #biodiversity #greenhousegasemissions #renewableenergy #carbonfootprint #reduce #reuse #recycle #climatejustice #climatecrisis #climateemergency #activism #oceanacidification #polaricecaps #wildlifeconservation #cleanenergy #climatehope
Related Questions, Words, Phrases
how fast are glaciers melting | what is the rate of glacier melting | how quickly are glaciers melting | how rapidly are glaciers melting | what is the speed of glacier melting | how fast are ice caps melting | what is the pace of glacier melting | how much are glaciers melting per year | how much are glaciers melting annually | what is the rate of ice melt | what is the rate of ice loss | how much ice is melting every year | how quickly are ice caps melting | how much are ice caps melting per year | how much are ice caps melting annually | what is the speed of ice melt | how fast are polar ice caps melting | how fast are mountain glaciers melting | what is the pace of ice melt | how quickly are polar ice caps melting | how quickly are mountain glaciers melting | what is the rate of mountain glacier melting | what is the rate of polar ice cap melting | what is the rate of arctic ice melt | what is the rate of antarctic ice melt