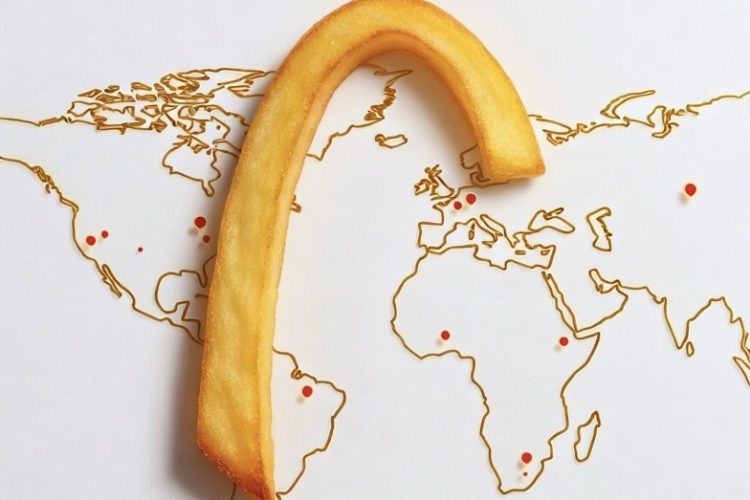
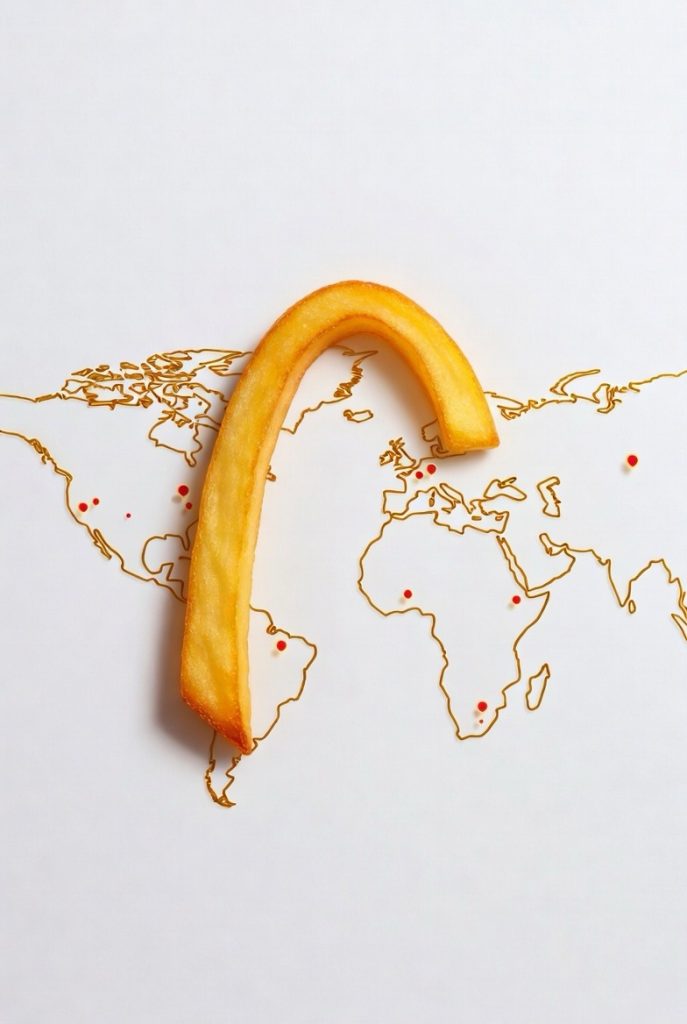
McDonald’s operates approximately 41,800 restaurants worldwide as of early 2026, spanning over 100 countries with the United States home to about 13,500 locations and strong growth in Asia-Pacific, including more than 5,500 in China alone. The company aims to reach 45,000 restaurants by 2030 through strategic expansions, digital innovations, and a resilient franchise model. For its iconic burgers, McDonald’s sources 100% pure beef from trusted suppliers like Cargill, OSI Group, Lopez Foods, and Keystone Foods, drawing from key regions including North America, Australia, New Zealand, South America, and Europe. Emphasizing transparency and responsibility, the chain pursues deforestation-free beef sourcing by 2030, with 85% compliance already achieved in priority areas, while investing in regenerative agriculture to support soil health, biodiversity, and ethical practices throughout its global beef supply chain.
Long Version
McDonald’s Worldwide Reach: Decoding the Numbers and Beef Supply Secrets
Ever stopped to ponder the sheer magnitude of McDonald’s as a global powerhouse? From the question of how many McDonald’s restaurants worldwide to the intricate details of where McDonald’s gets its beef from, this fast-food behemoth operates on a scale that’s both awe-inspiring and meticulously managed. As the ultimate resource on this topic, we’ll unpack every facet, offering fresh perspectives on its expansive network, supply chain dynamics, and forward-thinking strategies. Whether you’re intrigued by the global McDonald’s count or the sustainability behind its burgers, this guide delivers actionable insights to deepen your understanding of how this icon sustains its empire.
McDonald’s isn’t merely a chain—it’s a symphony of operations blending efficiency, adaptation, and responsibility. With billions served annually, its story reveals lessons in scalability and ethical sourcing that resonate beyond the drive-thru. Let’s delve into the core elements that define its dominance.
Mapping the Global Footprint: How Many McDonald’s Locations Exist Today?
The query “how many McDonald’s in the world” yields a staggering answer: As of early 2026, McDonald’s boasts approximately 41,800 restaurants operating worldwide, a figure that underscores its unparalleled presence in over 100 countries. This represents a modest yet strategic growth from about 39,000 in 2020, reflecting a post-pandemic rebound and targeted expansions into underserved markets.
Regional Distribution and Market Insights
Breaking down McDonald’s restaurants worldwide by region highlights strategic priorities and cultural integrations. The United States leads with around 13,500 outlets, where density supports innovations like app-based loyalty programs and 24/7 operations.
Venturing abroad:
- Europe: Approximately 9,800 locations, with Germany at over 1,400 and France close behind at 1,500. These markets emphasize premium offerings, such as McCafé expansions, to align with local tastes.
- Asia-Pacific: A hotspot for growth, featuring about 10,500 restaurants. China tops the list with more than 5,500, driven by digital integrations, while Japan maintains around 2,900 with unique items like teriyaki burgers.
- Latin America, Middle East, and Africa: Collectively around 4,500, with Brazil at nearly 1,000 and growing presences in Saudi Arabia and South Africa. Here, menu adaptations like halal certifications and vegetarian alternatives cater to diverse demographics.
- Other Key Players: Canada and Australia each hover near 1,400, benefiting from strong franchise models that foster community ties.
This distribution isn’t random; McDonald’s analyzes demographics, economic indicators, and competitor landscapes to optimize the number of McDonald’s locations, ensuring accessibility without oversaturation.
Expansion Tactics and Emerging Trends
McDonald’s global locations have evolved through a blend of organic growth and acquisitions, with a 2025 addition of about 1,800 new stores marking a 4.5% increase. Looking ahead, the company targets 45,000 by 2030, prioritizing high-potential areas like Southeast Asia and Africa.
Core strategies include:
- Digital Transformation: Leveraging AI for site selection and operations, enhancing efficiency in new builds.
- Franchise Empowerment: With 93% franchised, local entrepreneurs drive adaptations, from eco-friendly designs to region-specific promotions.
- Resilience Amid Challenges: Navigating inflation and supply issues, McDonald’s pivots to compact formats like kiosks in urban hubs.
These efforts ensure the worldwide McDonald’s count remains dynamic, balancing ambition with practicality in a competitive landscape.
The Backbone of Burgers: Unveiling McDonald’s Beef Sources
Central to McDonald’s appeal is its commitment to quality, prompting questions like “McDonald’s beef source” and “where does McDonald’s beef come from.” The company sources its massive global beef supply from a vetted network, emphasizing 100% pure beef patties without preservatives, fillers, or extenders. This supply chain handles billions of pounds annually, sourced responsibly to meet rigorous standards.
Primary Suppliers and Their Contributions
McDonald’s beef suppliers are industry leaders, selected for reliability and alignment with brand values. Key partners include:
- Cargill: A cornerstone for processing, focusing on large-volume, high-quality beef with advanced traceability systems.
- OSI Group: Operates globally, specializing in custom patties and pioneering sustainable farming integrations.
- Lopez Foods: Excels in fresh grinding and distribution, ensuring consistency across North American markets.
- Keystone Foods (part of Tyson): Handles international logistics, emphasizing animal welfare in its operations.
- Other Regional Allies: Firms like JBS in South America and independent processors in Europe round out the mix.
These collaborations undergo regular assessments, fostering innovations like portion-controlled patties that minimize waste.
Sourcing Regions and Operational Flow
McDonald’s global beef supply draws from multiple countries to ensure year-round availability and cost efficiency. Major contributors are:
- North America: The U.S. and Canada provide the bulk for domestic needs, with ranches adhering to grass-fed protocols for flavor enhancement.
- Australia and New Zealand: Renowned for export-quality, grain-finished beef that meets McDonald’s tenderness criteria.
- South America: Brazil and Uruguay supply significant volumes, though with strict oversight to address environmental concerns.
- Europe: Local sourcing from the U.K., Ireland, and Poland reduces carbon footprints and supports EU regulations.
The journey involves ranching, feedlot finishing, and processing under HACCP guidelines. Traceability tech, like blockchain pilots, allows tracking from farm to restaurant, bolstering McDonald’s meat origin transparency.
Advancing Sustainability: Ethical Dimensions of McDonald’s Beef Supply Chain
In an era of heightened awareness, McDonald’s beef supply chain sustainability stands out as a proactive area. The company integrates eco-friendly practices to mitigate impacts, offering a model for industry peers.
Combating Deforestation and Promoting Regeneration
McDonald’s aims for deforestation-free beef by 2030, with 2025 reports showing 85% compliance in priority regions like the Amazon basin. Initiatives include satellite monitoring and supplier incentives for conservation.
Regenerative agriculture takes center stage, with partnerships investing in soil restoration across millions of acres. For instance, collaborations with the Nature Conservancy promote cover cropping and biodiversity, yielding dual benefits of environmental health and resilient yields.
Prioritizing Animal Welfare and Community Impact
Standards mandate humane handling, including low-stress transport and audited facilities. McDonald’s supports the Global Roundtable for Sustainable Beef, advocating for benchmarks that elevate welfare across suppliers.
Balanced considerations include critiques from environmental groups pushing for reduced beef reliance, yet McDonald’s incremental steps—like emissions targets and alternative protein explorations—demonstrate commitment. This approach not only addresses McDonald’s ethical beef sourcing but also empowers farmers through training and fair pricing.
Navigating Obstacles and Embracing Innovation
The scale of McDonald’s operations invites complexities, from volatile commodity prices affecting beef costs to geopolitical factors disrupting supplies. Innovations counter these: Predictive analytics forecast demands, while diversified sourcing buffers risks.
Future-wise, expect deeper integrations of plant-based options and tech-driven efficiencies, ensuring the McDonald’s beef suppliers evolve with consumer preferences for health and sustainability.
Key Takeaways: Scale Meets Stewardship
Ultimately, McDonald’s operates around 41,800 restaurants worldwide, fueled by a robust global beef supply from trusted sources like the U.S., Australia, and beyond—all woven into a fabric of sustainability and innovation. This exploration of the number of McDonald’s locations and the nuances of its meat sourcing illuminates a brand that’s as adaptive as it is influential. By blending vast reach with responsible practices, McDonald’s continues to serve not just meals, but a vision of balanced progress that resonates globally. Armed with these insights, readers can appreciate the depth behind every bite.